What is Electrocautery mole removal?
Moles often appear in your childhood or teens and range in color from your natural skin tone to pink, brown, or black. People with darker hair or skin tend to have darker moles than people with fairer hair or skin. Moles can be flat or raised from the surface of your skin. Your healthcare provider might refer to your mole as a nevus (“nee-vis”) or a group of moles as nevi (“neev-eye”).
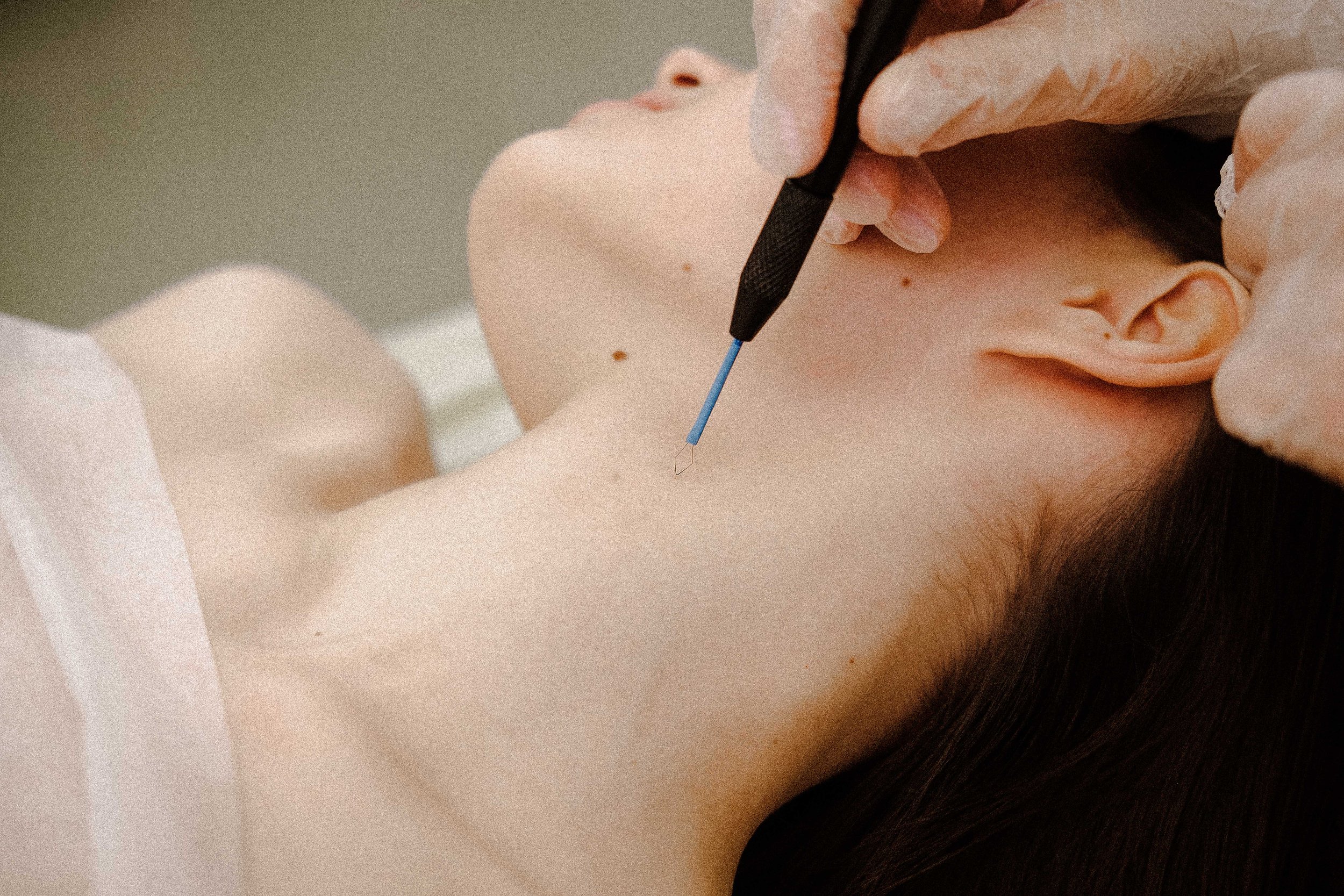
It’s normal to have about 10–40 moles by the time you’re an adult. Some moles grow slowly and may lighten or disappear over time. Most moles are harmless, but you should see your healthcare provider if you have any concerns about the appearance of a mole, or if it changes color or shape, becomes itchy, or bleeds.
Sometimes, moles are skin cancer or precancerous. If your mole is itchy, bleeds, isn’t round or oval, or you notice changes in its appearance, contact your healthcare provider.
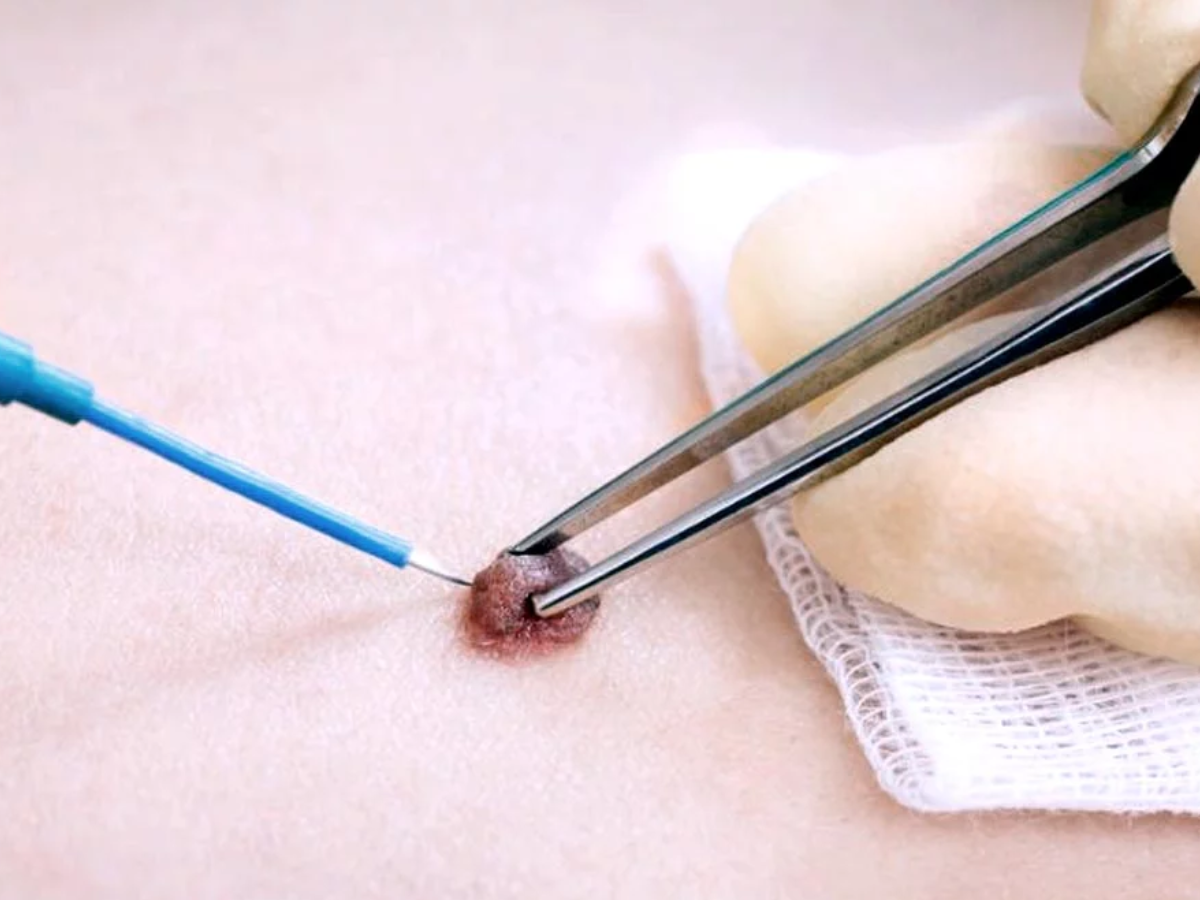
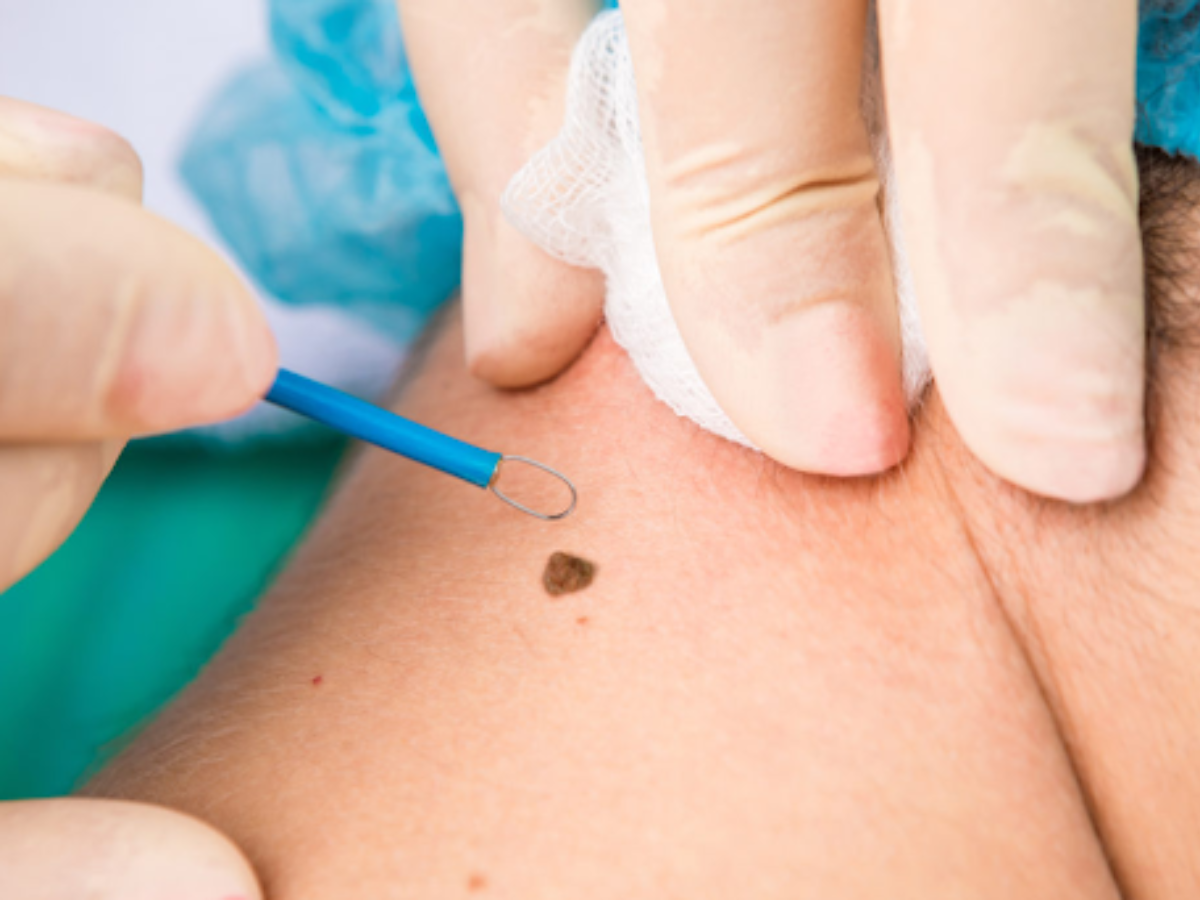
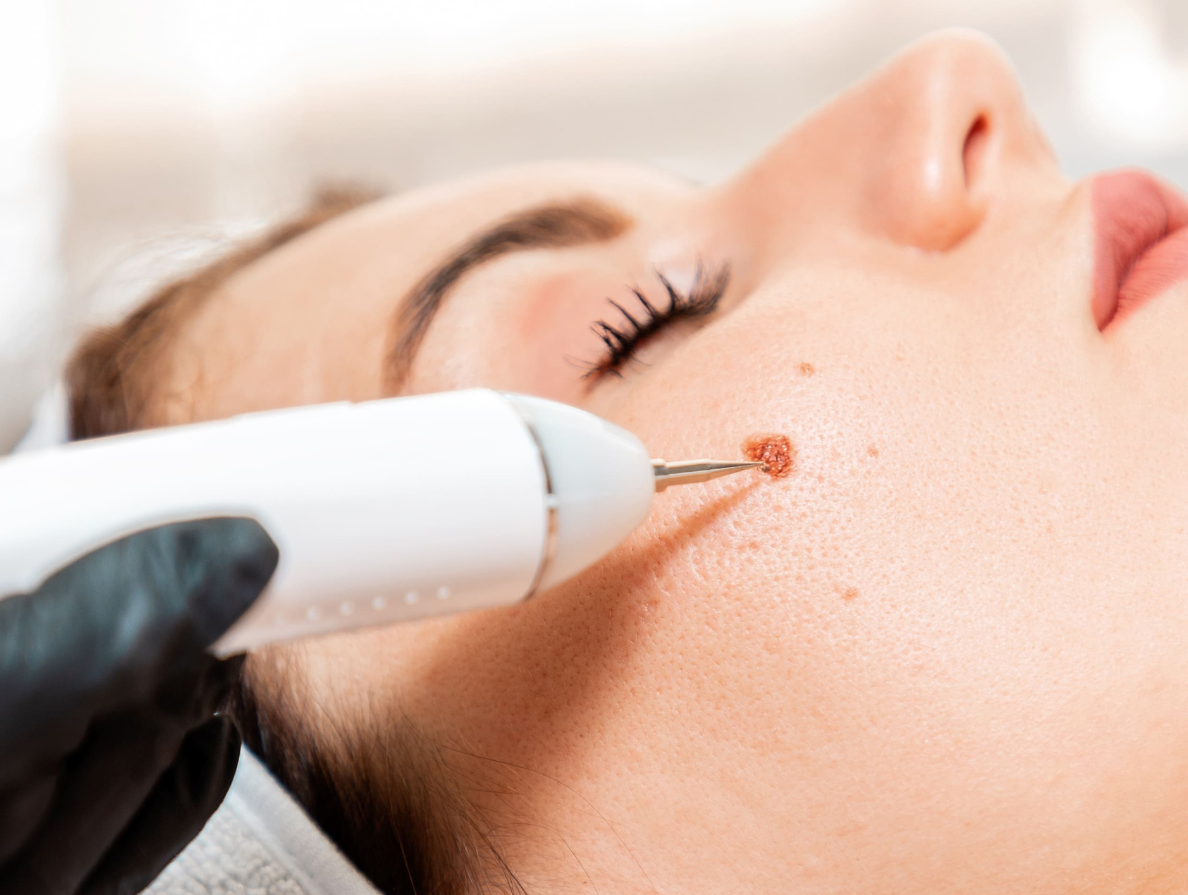
Why is mole removal done?
Mole removal treats atypical moles anywhere on your face, neck, arms, legs, or torso. Your healthcare provider may recommend removal of an atypical mole so they can run a test (biopsy) to see if the growth is cancerous (malignant) or precancerous. And if your dermatologist can remove the mole and achieve good margins (the area around the mole), mole removal may serve as a curative treatment for skin cancer that hasn’t spread.
Your healthcare provider may also remove a mole if you’re unhappy with its location or appearance.
Who needs to have this treatment?
Most moles don’t require treatment. But you might want to have a mole removed if you’re unhappy with how it looks or feels. Talk with your healthcare provider if you’re concerned about a mole. Generally, moles are removed if your provider suspects they might be cancerous or for cosmetic reasons.
